GPS Is Smartening Up Your Cell Phone
location based services
There's a good chance that you are, right now, carrying around a tiny device that's picking up faint radio signals from space and keeping track of your location. It's a Global Positioning System -- or GPS -- receiver, built into your cell phone. A hundred million or so people in the United States have those devices, but few, up to now, have been able to use them.
Selling the GPS Idea
Cell phone companies didn't originally want to put GPS receivers into cell phones. But several years ago, the Federal Communications Commission required them to come up with a way to locate their customers for rescue workers and 911 calls.
Some companies, such as Cingular, adopted technology that locates a cell phone by analyzing how its signal is picked up by different cell towers. Others, including Verizon, Sprint, and Nextel, decided to install a GPS receiver in every cell phone. This generally determines location more accurately, although it doesn't work as well indoors or in dense cities.
When Chuck Fletcher, of Montclair, N.J., heard that GPS technology was showing up in cell phones, he started dreaming of ways to use it.
"GPS is pretty magical technology, actually," Fletcher says. "Just the idea that there are satellites out there floating up in the sky that are put up specifically to help you figure out where you are."
He found a programmer named Jason Uechi who had more experience working with cell phones. Together, Fletcher and Uechi created Mologogo, an application which uses GPS to show users where their friends are -- in real time.
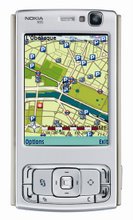
When Fletcher pulls out his phone and selects Mologogo, it displays a map of the streets around him while a dot shows his location. It also shows where Fletcher's friends are, if they have Mologogo running on their cell phones. The phones all transmit their locations to a Web site, so Fletcher also can log in from any computer and find his friends online.
"You can search for your friends. You can even set it up to track one friend," Fletcher says. "And if that's the person you are interested in today because they're doing something interesting, you might want to set it up just to watch them, to see where they are and what they're doing."
When Fletcher and Uechi, collaborating via the Internet, first tried out Mologogo on their phones, they thought it wasn't working properly. The system showed both phones in almost exactly the same location. Only then did the two technology enthusiasts realize that they lived in the same town.
Fletcher says about 2000 people have downloaded the free Mologogo program onto their phones. One of them accidentally left his phone in a taxi one day. Instead of simply calling his phone, he sat down at his computer and watched the phone zoom back and forth across New York City, until the cab driver found the phone and called him.
"There's a lot of people who are using it as a way to just share their travels," says Fletcher.
Technology on Hold
Before you rush to your computer to download Mologogo, however, you should know that it doesn't work on most cell phones, because most cell-phone companies have locked away the information inside the phone where customers can't retrieve it.
Only one company -- Nextel -- has allowed programmers to retrieve geographic coordinates from the GPS chips in its phones. So Mologogo works on phones from Nextel or Boost Mobile, Nextel's prepaid service, but not on any others.
"If you can't talk to the chip, you're just -- you're kind of out of luck," Fletcher says.
Several cell phone companies, including Verizon and Sprint (which merged with Nextel last year), have now launched authorized services that use the GPS receiver to give you directions, or track your kids, but you have to buy those services and they're only available on certain phones.
Don Cooke, an executive at the mapping company TeleAtlas, wishes the cellular carriers were moving faster. Cooke is also the author of a book called Fun With GPS, which suggests using GPS devices to map your hiking trails or figure out where your dog goes when it disappears for hours on end.
"A lot of people like me are very frustrated, because we can't get at the internal coding of the cell phone to be able to use it," Cooke says.
But Mary Foltz, director of wireless data business products for Sprint-Nextel, says there are good reasons to keep your whereabouts under wraps.
"Location information is incredibly sensitive and incredibly private," Foltz says. "So our No. 1 concern was to contain that information so that if it's being provided, it's only with the customer's consent, and in a way where they have full control over it."
Tracking More Than Just People
But many in the mapping business say there's another reason, apart from privacy concerns, that the cell phone companies are keeping such tight control over location information: The companies are hoping to convert it into profits.
Some of the new services now hitting the market show that GPS receivers are good for a lot more than tracking people. Among them is something called Smarter Agent. It's one of the new authorized services that you can buy if you are a Sprint/Nextel customer.
Brad Blumberg, the CEO of Smarter Agent, is happy to show off the service on his own phone. He pulls it out, selects "Smarter Agent" from a menu on the phone, and after a minute of waiting, the phone displays a tiny map of the area where Blumberg is standing. It happens to be on Capitol Hill, in Washington, D.C., right in front of the Folger Shakespeare Library.
Blumberg points to ten little blue houses, arrayed on the map. Those are the houses closest to this location that sold within the last three years. Blumberg selects one, and more information appears.
"That property sold for $850,000," Blumberg announces, sounding amused. "It's getting a little expensive back here. I remember when this neighborhood was not so expensive."
Blumberg can walk around any major city in America, look at houses in front of him, and find out what they're worth. And in the future, it might not be just prices.
"What's really dear to my heart is, we'd be able to stand here and I'd be able to learn about the architecture of the buildings in front of me. Based on your interest, you'd be able to pick, say, history, and all of a sudden there would come streaming: 'You want to know what was here in 1700? Or 1600?' And if it's 1700, maybe we send you a picture of the area."
Cell phones could, in fact, be set up to retrieve any information that's stored in a database somewhere. So you could stand on a corner and get phone numbers of people on that street, the median income of the neighborhood, or, if you want to frighten yourself, you could see whether any murders were committed nearby. The cell phone could become your guide to things you can't see in the world around you.
Technology
Somebody's Watching You -- and It's Your Cell Phone
by Melody Joy Kramer
NPR.org, September 18, 2006 · There's a ball game you're dying to see. It's on a Tuesday. At 1 p.m.
So you call your boss, fake a cough, and toss in a sneeze for effect. "I have a fever," you say. "I'm highly contagious. I'll stay home."
Come 1 p.m., you're at the ballpark, feeling great about the ruse. Only back at the office, your slightly suspicious boss has decided to use the latest software to see whether you were telling the truth. The software connects to your phone, which you've brought to the game, and the phone's GPS device reveals that you're at the stadium and not home in bed.
Currently, 100 million cell-phone users have a GPS device in their phone that can pinpoint the phone's location. In addition, software companies use GPS coordinates to retrieve information stored in public databases. Point your cell phone at a house, for example, and it could tell you the phone number -- or the average home price in the neighborhood.
Cell phone companies are reluctant to release such data because of privacy concerns. But one company -- Sprint/Nextel -- has always allowed access to the geographic information from the chips in its phones.
At the moment, Sprint/Nextel customers can download third-party software that allows them to broadcast their location on the Internet to their friends. This software is opt-in: Customers decide who can see their coordinates.
Indeed, strict privacy regulations govern any third-party software application developed for Sprint/Nextel authorized services.
"The vendor or the applications would be covered by the Sprint [privacy] agreement," says Jenny Walsh, a Sprint spokeswoman. Sprint will not share information about your location without your consent unless your life is in danger --say, if you call 911.
But if you sign up for third-party software that's not authorized by Sprint/Nextel, your privacy is not guaranteed. To protect yourself, privacy experts suggest reading all privacy policies for any software you download to your mobile phone -- there should be language indicating whether your information could be sold to a vendor.
And then there's the matter of your work phone. Companies are not obligated to reveal whether they have GPS software for the phones they give employees. This worries Lauren Gelman, associate director at the Center for Internet and Society at Stanford University.
"I think where you are is a particularly private thing," Gelman says. "And we understand that the people in our vicinity [know] where we are but it's very different when people who we can't see know where we are."
Of course, technology can only go so far. If only ballgame boy had been wise enough to leave his company cell at home on his pillow.
Related NPR Stories
Jan. 27, 2006Cell Phone Calls and Privacy
Feb. 13, 2006Crafting a Smarter, Gentler Cell Phone
Feb. 25, 2006New Kind of Map Could Help Emergency Response
July 31, 2006Census Bureau Adopts GPS to Find American Homes
Aug. 17, 2006Taxi Drivers Wary of GPS Tracking Plan
Aug. 29, 2006Technology Lets Parents Track Kids' Every Move
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)





























No comments:
Post a Comment