Location based services on the rise
The demand for location based services is continuously increasing as operators upgrade their networks to 3G
Location-based services (LBS) have witnessed all the ups and downs of trade and finally are at a cusp of technological prowess and business friendly application development. Faster 3G networks, stable position determining technologies, enhanced handset capabilities, increased user acceptance of data relevant services and a mass market approach of service providers have all contributed to the rise of LBS. Add to this, the availability of Location API support in ubiquitous java application platform (J2ME) on mobile phones opens a window into the innumerable opportunities in application development.
ZDNet research believes that LBS applications will have a marke of around $771.9 million by 2010, with a consistent CAGR of 10.5% in Asia alone. In another generic research by Juniper, the total available market for mobile location based services would be $8.5 billion by the end of 2010. The largest geographic market will be Asia Pacific, with Europe and North America second and third respectively. The demand for location based services is continuously increasing as operators upgrade their networks to faster and more capable 3G which promises to be a nirvana for speed and connectivity.
What is a Location Based Service (LBS)
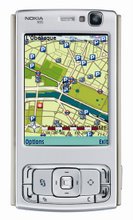
The World is full of information with myriad data resources. But, data becomes useful only when packaged in the right format and presented in a right context. One significant data source is ‘Geographical Location’. Information based on location of a consumer and services derived with such data are termed as Location Based Services. These services could be weather, traffic, events, hotels, petrol pumps, adjacent ATM locations and such other user relevant facts presented on a convenient interface. Location based services answer simple questions like “where you are, what is around you and how you could get there.” Personalization is a key driver for the success of any application. Currently, most of the devices that we use are often unaware of their current location. A mobile phone may never know that its user has traveled from one country to the other and may be unaware of the change in time zones. Location awareness adds an important facet to data centric applications and this in turn generates numerous possibilities. Location information is especially important in case of emergencies, E911 in North America and E112 in Europe are perfect examples where location forms the most essential and central information to reach the person needing some help.
With mobile telephony, communication is no longer restricted by geographical boundaries. Handheld mobile devices provide useful information about the user’s location and this can be intelligently used to track his preferences and interests. This is also an important area of research and advancement in both academic and industry circles. Today’s mobile phones with their compact size and rich processing power present a great opportunity for location aware applications.
Tech behind technology
- Mobile operator information
Currently, most mobile operators around the world provide some basic location information in form of Cell ID, available free of cost for each mobile user. This information could be further utilized to derive services like informatiobn on shops, restaurants, ATM, etc in the 'Cell' (adjacent area) and pass it onto the user, based on his preferences. An obvious problem in such a scenario is the size of the Cells. The Cell size could vary from 2 to 20km depending on a number of factors like density, urban/rural areas and so on. Mobile operators also posses advanced equipment to determine the exact location of the user, but this is generally made available at a predefined cost to third party application developers. The mobile user’s consent to track him is also an important aspect that is taken into consideration.
- GPS
GPS or Global Positioning system is a satellite based technology. A constellation of more than two dozen GPS satellites broadcasts precise timing signals by radio to GPS receivers, allowing them to accurately determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude) in any weather, day or night, anywhere on Earth. This satellite information is currently available free of cost provided the user possesses a GPS receiver. A major drawback that is often cited is its high sensibility to multi-path and interference, which are the two main sources of errors in range and position estimations. In simpler terms, GPS does not work indoors i.e., inside buildings, houses or any closed structure. - Assisted GPS
Assisted GPS combines the information obtained from the mobile operator along with that obtained from satellite to approximate the location of the user. It is a form of GPS which uses cell towers to supplant the on-phone hardware and assist when signal levels provided by GPS are low. Sometimes, a GPS received can be planted in a Base station (BS) itself and as this is sufficiently close to the location of the user, the data received by this location is fairly accurate for mobile user. Base stations’ receivers are generally located in such a way that they are constantly visible to the satellite.
Read More Page(s)
Location based services on the rise
Advantage LBS
Did we forget Privacy?
Email this article
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)





























No comments:
Post a Comment